Visualise yourself riding a bike, and lo and behold, you get a flat tyre out of nowhere.
Now, you are in a dilemma: fix it yourself or get scammed by letting someone else do it because you don’t know right from wrong.
That’s why, when you own an e-cycle or any vehicle for that matter, knowing the basic ins and outs is of paramount importance. It’s crucial for any cyclist, whether they’re only a casual rider or a hardcore adventurous person looking to travel with an EMotorad e-bike across the globe.
A rough idea will create connectivity between you and your loyal horse, or, in this case, a steel horse.
It’s time to get down to the nitty-gritty of a bicycle wheel and unravel its anatomy. Maybe someday, this knowledge will prove to be beneficial in some way or form.
Let’s wheel in!
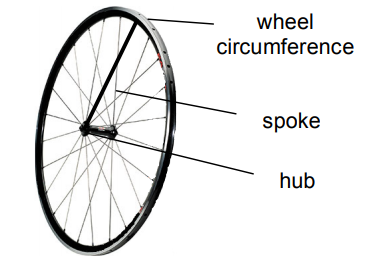
The Hub: The Heart of Your Wheel
The hub is like a bicycle's heart or the heart of the wheel.
The hub sits at the wheel's centre, attaching a wheel to the bicycle through the common part called the axle, which holds the centre of action.
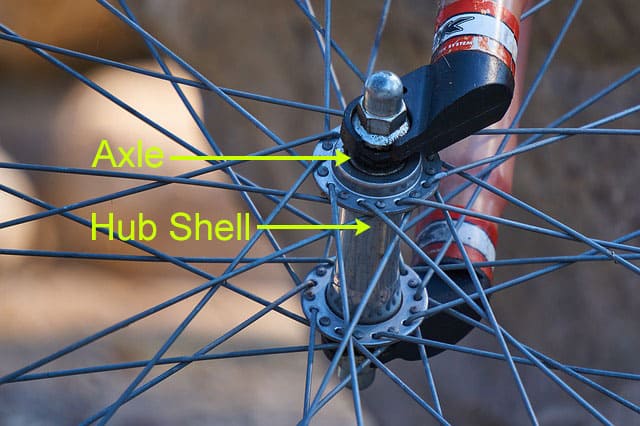

Parts of the Hub:
Axle: A rounded bar that runs right through the heart of a wheel’s hub and gets it spinning
Bearings: Tiny beads that keep the wheel spinning. Though not the most impactful, ball bearings are commendable devices in this respect.
Hub shell: The outer covering that contains them all
A bad hub can spoil the whole wheel, but thankfully, all high-end e-bikes like the ones from EMotorad come with hubs made to last in terms of quality and performance.
Spokes: The Wheel’s Support System
It is the duty of the spokes to provide structure and strength to your wheels.
Hollow thin rods come together to connect the hub to the rim, ensuring proper distribution of weight in front and back for a smooth ride.
Fun Fact: A wheel stays round and doesn't wobble because of the tension in the spokes. If one spoke slips, the whole wheel can go out of true.
It’s like a Jenga tower but with more physics.
To know more about why spokes are so important to an e-cycle, check out this blog: What Are Spokes in a Bicycle Wheel?
Spokes can be made of different materials like steel or carbon fibre, and the number of spokes varies depending on the type of bike.
EMotorad has precision-designed wheels to ensure the right tension for stability and strength.
The Rim: The Outer Circle
The rim, referred to as the wheel's outer edge is utilised to keep the tyre in place. It is the exact point where rubber meets the road.

Types of Rims:
Clincher Rim: This is commonly used with tyres and inner tubes
Tubeless Rim: Those without tubes are more environmentally friendly, resistant to punctures, and with less rolling resistance
Aero Rims: Designed for aerodynamic performance, perfect for racers
Modern e-cycles like those from EMotorad often come with lightweight but strong rims that will boost both speed and endurance.
Tyres: Your Wheel’s Shoes
Tyres are the only element that comes between your smooth ride and firmly grounding your bike. In other words, they are the ultimate barriers against potholes and rough terrains.
Types of tyres:
Slick Tyres: These are best used for road biking, as they offer less rolling resistance
Knobby Tyres: Designed specifically for mountain bikes and known for their exceptionally deep tread patterns that make them difficult to slip off
Hybrid Tyres: A combination of both tread patterns, making it perfect for multi-faceted users
Hybrid tyres are often used by EMotorad in their e-cycles to make adventures wholesome.
Once your tyre has run flat, knowing how to remove and place a new tyre on the rim is a lifesaver.
Inner Tubes: The Air Carrier
If your tyres are the shoes, inner tubes are the socks.
Inner tubes take up the air, which makes your ride cushier. It doesn't matter if you do or do not have a tubeless bike - it's mandatory to keep the tyres inflated.

Pro Tip: Keep a spare tube and patch kit while riding long distances or touring. Also, know how to remove the wheel and replace the tube.
The e-cycles made by EMotorad usually have user-friendly and easy mechanism designs, which make the unmounting of the wheel quite effortless.
Nipples: Tiny but Mighty
Little threaded nuts use the central part of the rim to keep the spokes in place. Without them, the tension in the spokes would be gone.

But then, of course, what matters most would be the fact that a spinning wheel due to uneven tension could result in a loose nipple. You have to observe and tighten them.
The Valve: Inflate and Conquer
Your inflating tyres can still look fine by using the correct valve.
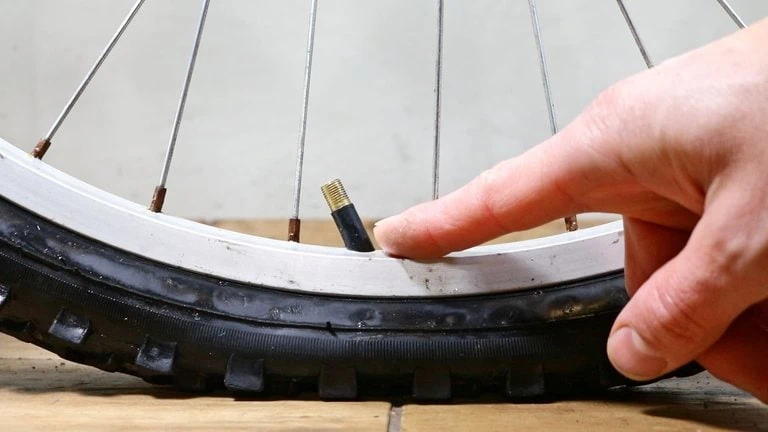

The three types of valves are:
Presta Valve: Slim, used in high-pressure road bike tyres
Schrader Valve: Wider, like the ones on car tyres
Dunlop Valve: Sturdy, broad design, mostly used on inner tubes of cycles
Whenever you are considering getting your tyres pumped in a gas station or using a portable pump, It’s critical to remember the type of valve you are dealing with.
EMotorad builds their bikes with simple-to-manage valve systems.
Braking Surface: Stopping Power
An important part of the rim is the braking surface, where the brake pad meets the rim.
It makes the most difference in traditional rim brake systems, especially for braking properly.

Modern bikes typically use disc brakes, and the concentration of braking energy changes from the rim to the rotor, providing more efficient braking even in wet or muddy surface conditions.
Disc Brakes and Rotors: The Modern Stopping System
Disc brakes have really revolutionised this sport.
The rotor, a flat metal disc attached to the hub, is clamped by the calliper when braking to prevent the wheel from turning.
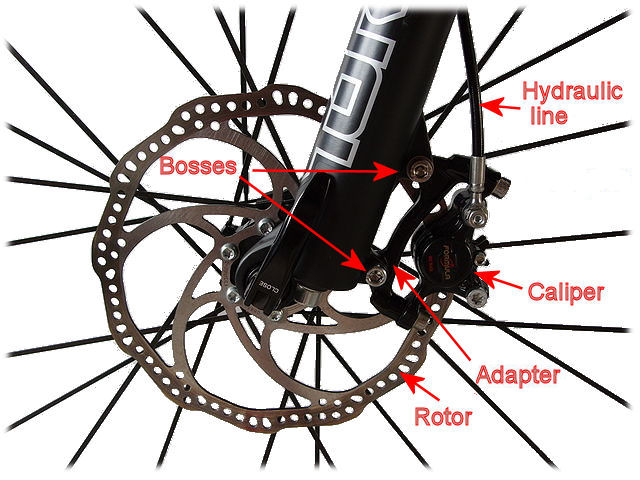
Advantages of Disc Brakes:
Better braking power in all conditions
Less wear and tear on the rim
Improved control and safety
Almost all EMotorad bikes are equipped with high-quality disc brakes for a safe and smooth journey.
Why It All Matters
When you understand how a bicycle wheel works, you are not just learning the dynamics of a bike but all the must-know factors.
It is nice to know what to do when patching a puncture, truing a wheel, or upgrading a bike.
Then, you can ride and understand your riding capability. The more knowledge you have about your parts and how they work together, the more you become a confident and capable cyclist.
If knowing about e-cycle wheels interests you more, here is the perfect blog for you: Electric Cycle Wheels Guide: Features & Maintenance for a Smooth Ride
Brands like EMotorad offer today's e-cycling perfection with high-end technology and well-thought-out designs. Their e-cycles are indeed designed to keep the stress away while you enjoy yourself on a ride.
Conclusion
From a modest spoke to a powerful disc brake, every component in the wheel of a bicycle is an essential factor in ensuring you keep rolling.
You can use the knowledge to troubleshoot any unusual problems and also have a wider value attached to the wonder of engineering under you.
Next time, pay some respect to your wheels when you jump onto your e-cycle and every machine part that works in harmony.
For those searching for a ride that is as reliable as it is innovative, EMotorad has what you need. So when it comes to cycling, knowledge is power and, in the same manner, good wheels.








About Us
Blogs
News
EM Stories